[ad_1]
An ELI5 abstract of how and why SVB failed, and whether or not there have been any crimson flags that retail buyers might have used to foresee this. What can we, as buyers, study from this incident?
Spoiler alert: it will have been extremely troublesome. This text examines how, in an alternate actuality, SVB could not have collapsed in any case.
Final week, we watched because the 16th largest financial institution within the US collapsed. Up till final Friday, it was the preferred bank for startups and tech firms, price over $200 billion and was a inventory market darling (having been advisable by numerous “gurus” and funding subscription companies) that benefited from the pandemic.
Till all of it got here right down to zero.
SVB a darling inventory for many
Silicon Valley Financial institution (SVB) Monetary offered banking companies to start-ups, who put their funds raised from non-public fairness or enterprise capital companies into the financial institution and use it for working bills, payroll, and so on.
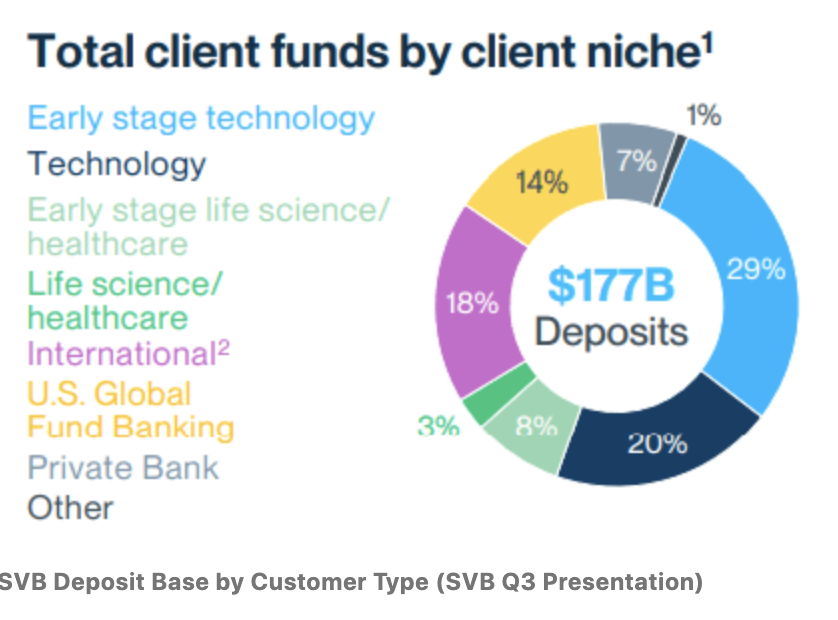
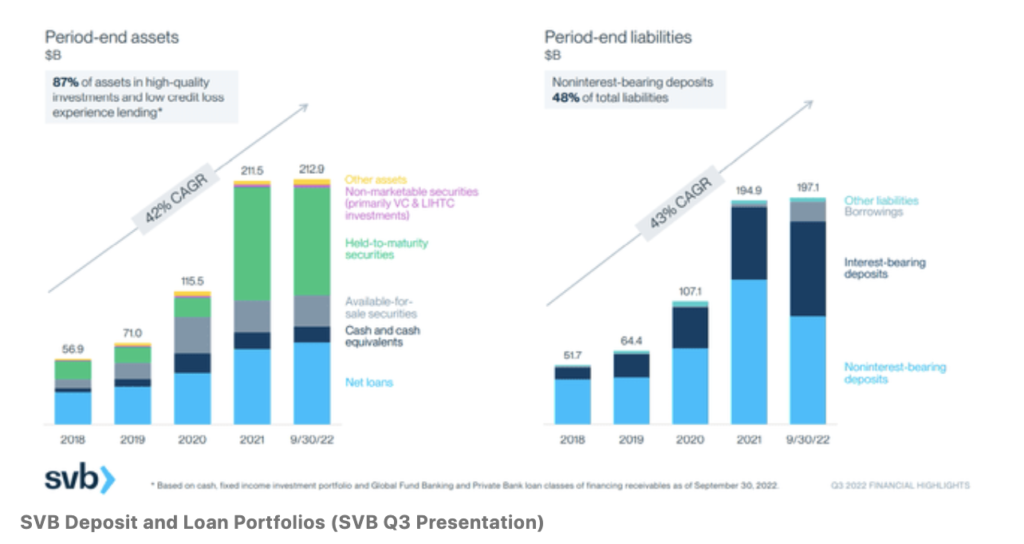
From a enterprise standpoint, SVB delivered super progress – from $6 billion in interest-earning belongings in 2007 to $210 billion in 2022 – an approximate 27% annual progress charge.
SVB’s progress in deposits and loans held regular at 10% – 20% within the years after the International Monetary Disaster. After which from 2018 onwards, the expansion charges accelerated to round 40% CAGR ranges.
This additionally translated into stable web revenue progress for the financial institution:
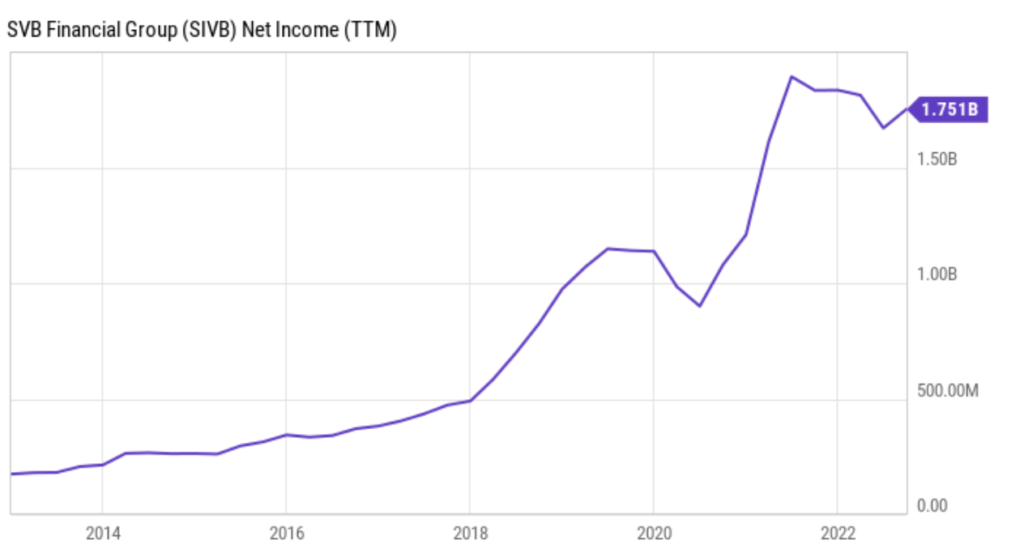
Consequently, SVB’s inventory usually traded at a premium to different banks due to its greater progress charges and excellent returns. Within the final decade, its return on fairness (ROE) outpaced even banking friends like JPMorgan Chase and Financial institution of America.
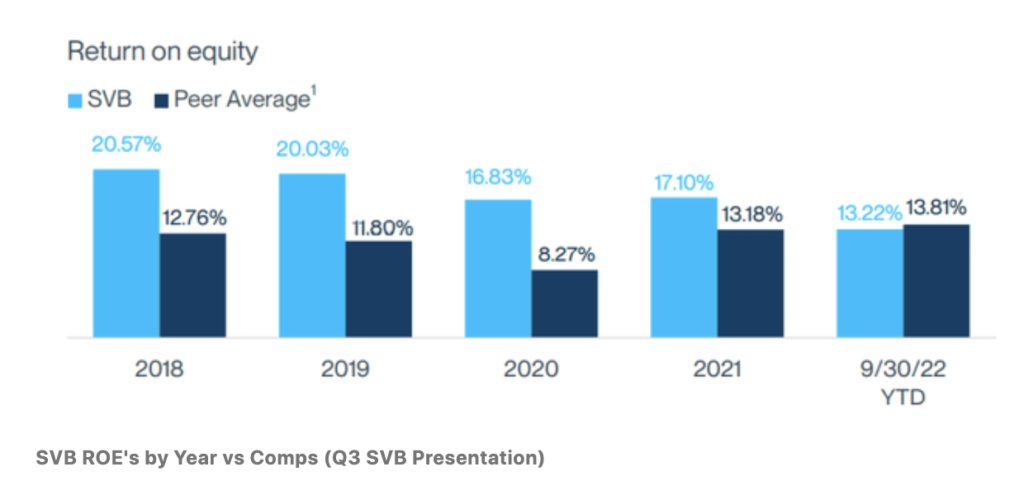
After the subprime mortgage disaster that induced the collapse of Lehman Brothers, buyers have been paying nearer consideration to the loans portfolio of banks. In SVB’s case, administration reassured buyers that their loans have been of low danger (though some had their doubts about whether or not a recession would ultimately result in the start-ups who loaned from SVB to default on their funds).
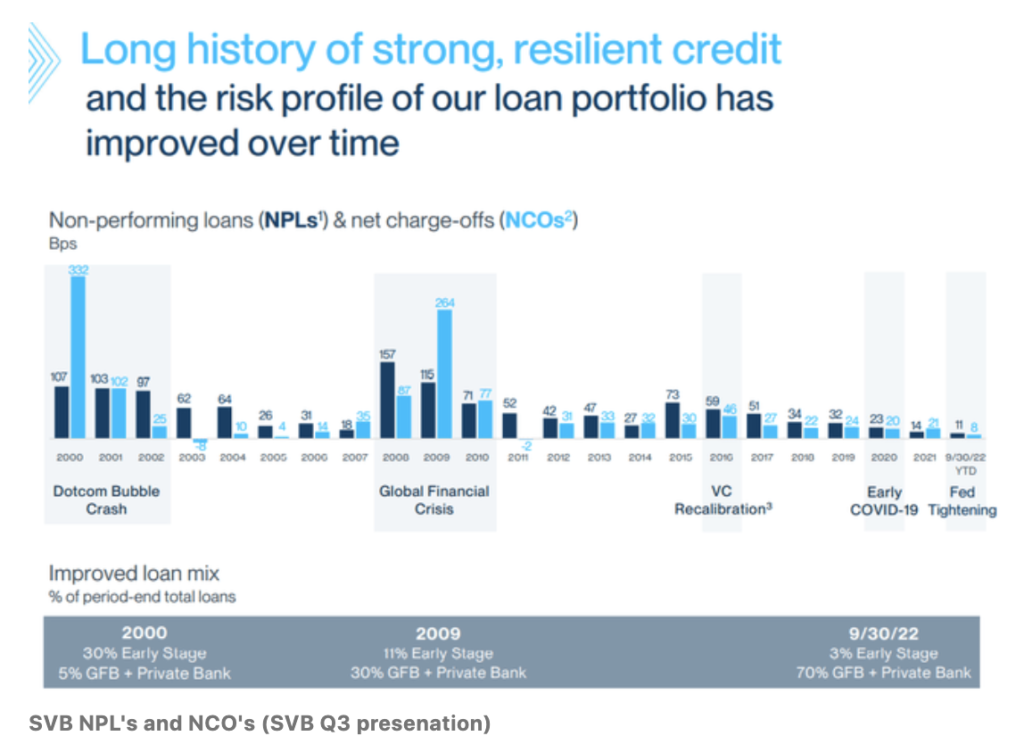
From a credit score perspective, SVB’s loans and bonds have been of a great credit score high quality; their information confirmed a low chance of default. However the crimson flags have been beginning to indicate.
In This fall 2022, SVB disclosed vital funding losses, which included a success of $27 million on the sale of $1 billion of US treasury bonds.
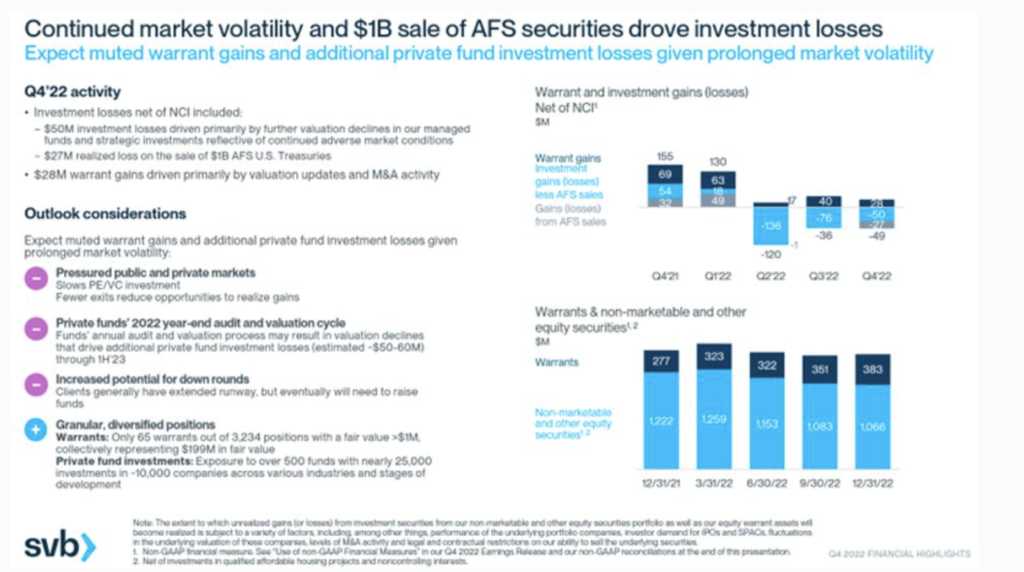
After which in March, the darling inventory crashed inside 24 hours.
How did Silicon Valley Financial institution collapse so shortly?
The way it was potential for such a big financial institution to break down in simply 48 hours, in much less time than what it took for crypto Terra Luna / USDT to go to zero final 12 months?
The first cause for SVB’s speedy collapse (in a minimum of 48 hours) was as a result of a financial institution run.
The secondary cause was as a result of management’s missteps (I counted at the very least 3).
In ELI5 (clarify like I’m 5) communicate, a financial institution run happens when purchasers wish to withdraw extra money from a financial institution than it has obtainable.
Financial institution run = when clients withdrawing cash > cash obtainable within the financial institution.
How did the financial institution run out of cash?
Properly, while you and I (depositors) put cash in a financial institution, the financial institution typically pays us (a low) curiosity on it whereas taking our funds to reinvest in monetary merchandise with the next charge of return – resembling via loans, equities, mounted revenue merchandise, and so on.
The distinction between what the financial institution pays us vs. what they earn = their income. And as of December 2022, SVB’s web revenue margin was nonetheless juicy at 22.05%.
However beneath the hood, the truth was that SVB had obtained a lot deposits throughout the previous couple of years (because of the run-up in VC funding via the pandemic) that it wasn’t capable of mortgage them out quick sufficient.
So, as a substitute of constructing dangerous loans (resembling to debtors with poor credit score however with excessive urgency wants), SVB determined to spend money on fixed-income investments – together with long-dated US authorities bonds – which have been a lot safer.
This was a administration misstep, though not but painfully apparent at the moment (given the alternatives).
Now, if rates of interest had remained low, this wouldn’t have been an issue. However then the Federal Reserve determined to boost rates of interest, they usually raised it quick.
Rates of interest went from successfully zero to virtually 5% in lower than a 12 months.
This induced 2 issues for SVB:
- The upper rates of interest additionally induced SVB’s mounted revenue investments to drop quickly in worth.
The second administration misstep right here was that SVB did not execute rate of interest swaps.
Bonds have an inverse relationship with rates of interest: when charges rise, bond costs fall. Therefore, SVB began seeing enormous losses on its bond portfolio. One technique to take care of that may be to hedge through rate of interest swaps, however in its FY2022 financial report, SVB reported virtually no interest rate hedges on its massive bond portfolio.
Whereas dangerous, this nonetheless wouldn’t have been an issue in the event that they have been capable of merely maintain till the bonds mature, as it will get again its capital then. Nevertheless, with low cost funding drying up, SVB’s clients have been additionally beginning to run into issues themselves, and wanted to withdraw its deposits to maintain their enterprise alive. Consequently, SVB’s deposit base began shrinking considerably, with non-interest-bearing deposits falling by 25% from December 2021 to September 2022.
Within the final quarter, SVB’s non-interest-bearing deposits declined by 36%.
As SVB began working out of liquid funds to satisfy these withdrawal requests, the financial institution had no selection however to begin promoting its bond investments. However who on earth would wish to purchase bonds with a low 1+% coupon charge after they can get the next charge T-bill right now? And therefore, SVB needed to promote the bonds at a steep low cost with the intention to liquidate its locked-up funds.
Then, on 8th March, SVB introduced that it had bought a complete of $21 billion of its investments at a loss with the intention to meet withdrawal demand, and that it was going to challenge fairness to boost further capital.

This was the third administration misstep: its communication failure.
In an alternate actuality the place the financial institution had managed its communications higher (and never in such a factual, simple method that clearly induced depositors to panic), we are able to solely think about one the place the financial institution run could not have occurred.
However SVB’s announcement spooked depositors, who began withdrawing their capital as a result of worries over the financial institution’s illiquidity. An enormous a part of the panic was additionally as a result of many depositors had greater than $250,000 in SVB accounts, which aren’t insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance coverage Company (FDIC).
Inside 24 hours, practically 25% of all of SVB’s deposits had been withdrawn (9th March).
On 10th March, the financial institution was seized by U.S. regulators and the FDIC ordered its instant closure.
The entire collapse unravelled in slightly below 48 hours, making it the largest financial institution failure within the US because the world monetary disaster.
Did the US authorities bail out SVB? No.
It was a painful weekend of ready with bated breath, however on 13th March, regulators stepped as much as assure all of the remaining deposits at SVB (together with uninsured funds) and unveiled a brand new Financial institution Time period Funding Program (BTFP).
The BTFP is designed for banks to have the ability to borrow funds backed by authorities securities to satisfy withdrawal calls for from deposit clients. This prevents banks (within the aftermath of SVB) from being pressured to promote authorities bonds or different belongings which have been dropping worth as a result of rising rates of interest.
With this transfer, it’s clear that the regulators know that the general public is spooked and are attempting to stop comparable financial institution runs at different establishments.
However solely the depositors are protected; shareholders of SVB and unsecured collectors aren’t.
This was not a bailout. The federal government is just not saving SVB – it would keep collapsed and wound up with its remaining belongings dispersed to clients and collectors.
Now that all of us perceive the backstory of SVB and the way it was potential for such a big financial institution to break down so shortly, what’s extra necessary is what we are able to possbily study from this. Therefore, the larger query right here is:
Might retail buyers have noticed the crimson flags?
Firstly, let’s be frank and acknowledge that not everyone seems to be able to understanding the (usually convoluted) banks’ monetary statements and notes. In the event you had checked out its balance sheet, there didn’t appear to be an excessive amount of to be involved about.
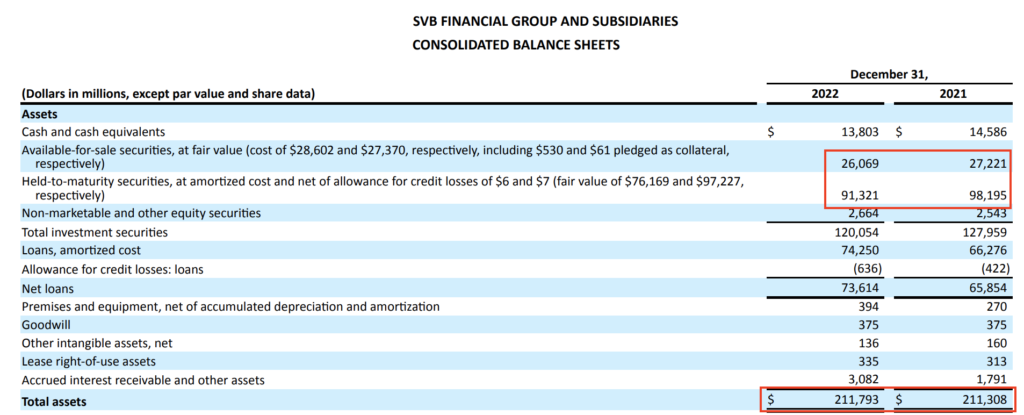
SVB was additionally not required to reprice their Held-To-Maturity (HTM) belongings based mostly on present market costs until they bought them, so the impression of its declining bond portfolio worth was not fully clear. One might solely guess, however bear in mind, this wouldn’t have been an issue IF the financial institution hadn’t wanted to promote bonds off to satisfy withdrawal calls for.
Just for the sharp-eyed buyers who bothered to look deeper into the notes to the monetary statements, web page 125 revealed a US$15.1 billion drawdown. In the event you had then deducted that from the reported worth of US$91.3 billion on the steadiness sheet , you might have then realized that the marked-to-market worth of all the HTM securities portfolio ought to have been US$76.2 billion as a substitute.
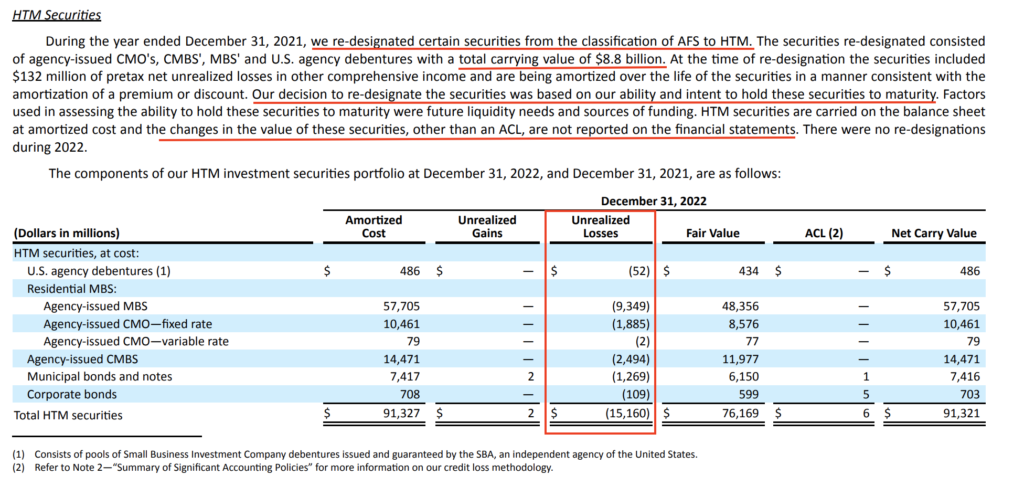
Even with this, you continue to wouldn’t have been capable of inform if the US$15.1 billion drawdown was as a result of HTM belongings maturing, or for another undisclosed cause. And in the event you seemed deeper, web page 64 reveals you what the HTM belongings consisted of – not precisely sufficient to set off red-hot warning indicators.
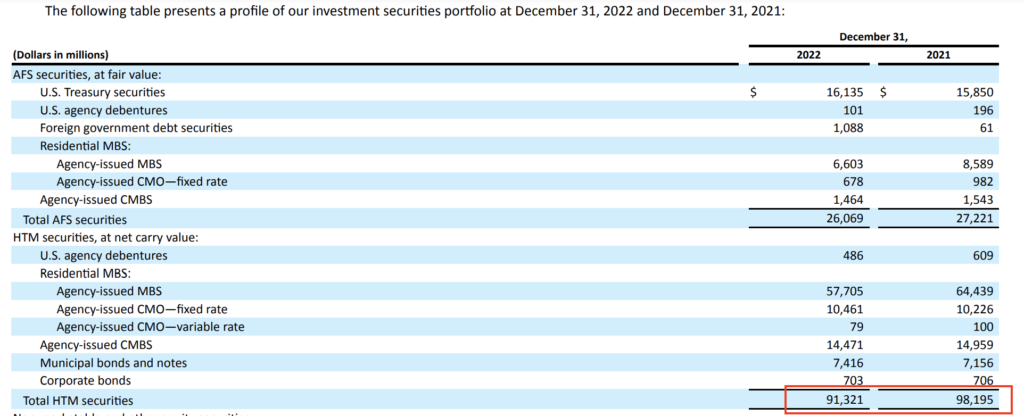
Some folks blame this on the relaxed danger administration necessities for banks beneath $250 billion in belongings, which was signed into legislation in 2018 by President Trump (which eased the necessities put in place within the aftermath of the GFC beneath the Dodd-Frank and the Client Safety Act).
Consequently, SVB was not required to disclose how much it had in high-quality liquid assets to help it cover net cash outflows (if depositors began withdrawing en masse), so it wasn’t one thing that retail buyers might decide up on.
Crucially, this implies there was no approach to know whether or not SVB had sufficient to stop a financial institution run, even when buyers have been involved that the start-ups SVB served would possibly begin withdrawing their funds. Dilution of current buyers was a extra possible state of affairs (as a result of SVB elevating new capital to fund liquidity wants).
What’s extra, 2 weeks earlier than SVB’s collapse, its CEO Greg Becker bought ~12,500 of his firm’s shares.
I suppose if an investor who had been vested and had been monitoring the corporate carefully, then recognizing the mix of crimson flags could have helped you to dump earlier than its collapse:
- SVB began reporting a narrowing deposit base since Dec 2021
- SVB’s clients are primarily tech companies and start-ups, who’ve been shedding employees and began defaulting over the previous 12 months.
- 16.5% of its (HTM) bond portfolio appeared to have declined in a single monetary 12 months. (An indication that solely eagle-eyed buyers with information of how HTM asset values work and are reported would have the ability to decide up on.)
- The Form 4 filing showing SVB’s CEO selling his shares to web $2.2 million
However even with that, it wasn’t really easy. In any case, the inventory was being touted as “low cost” by many subscription companies, and till Wednesday, Moody’s and S&P International had Silicon Valley Financial institution as an funding grade issuer – that means SVB had a low chance of default and loss severity.
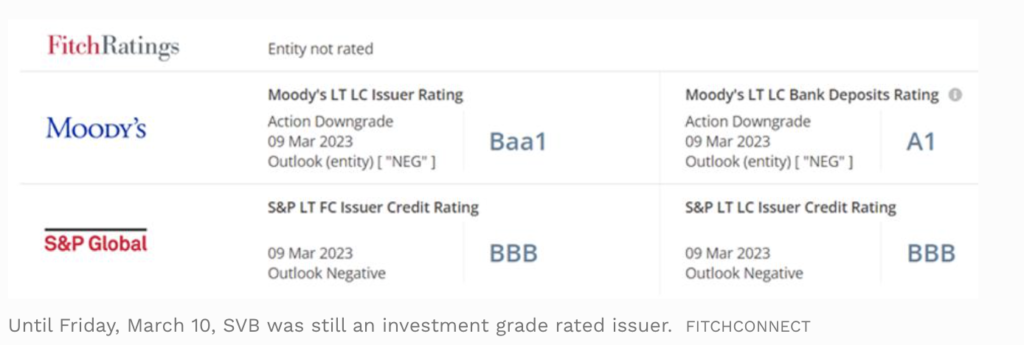
Solely Thursday (after the announcement) did Moody’s and S&P International modified their outlook on the financial institution from secure to detrimental.
TLDR (Hindsight Evaluate):
1. Traders had no approach to know whether or not SVB had sufficient liquid belongings to stop a financial institution run, as a result of prevailing regulatory reporting requirements.
2. SVB’s declining bond portfolio losses have been additionally unclear, because the financial institution wasn’t required to report it till bought.
3. There have been hardly any evident crimson flags in SVB’s loans portfolio, given the low ratio of non-performing loans.
4. The $2.2 million inventory sale by SVB’s CEO 2 weeks earlier than its collapse might have been a warning signal, however not a conclusive sign.
5. You would need to go in opposition to the prevailing sentiment that SVB was an undervalued, high-quality monetary establishment whose share value received battered solely due to the unlucky macro-economic local weather for tech companies.
6. Even Moody’s and S&P International rated SVB as funding grade i.e. one with a low chance of default and loss severity.
So might this have been foreseen? Not precisely.
The best way I see it, SVB’s collapse in the end comes right down to a mix of two essential administration errors:
- Investing within the incorrect belongings, after which failing to hedge that as rates of interest rose
- Poor dealing with of SVB’s communications (on 8th March), which spooked its depositors and triggered a financial institution run
Even in the event you have been a savvy investor who might spot #1, nobody might have predicted #2 with accuracy. In reality, nobody did.
It’s all the time straightforward to say (with hindsight accuracy) that there have been evident crimson flags that buyers missed. However after reviewing all the info and evaluation, I discover that this wasn’t essentially the case with SVB.
As you may see, it will have been troublesome to foretell SVB’s collapse with certainty. As a result of if #2 had been dealt with higher (and also you guys can debate over what that entails, resembling elevating funds from different banks or establishments as a substitute of promoting their bonds, and even tweaking the best way they made their announcement to make the illiquid state of affairs much less painfully apparent), a financial institution run could or could not have occurred.
And in that alternate actuality, who is aware of? SVB might need risen from the flames to reclaim its standing as a darling inventory in any case.
Writer’s Word: I don’t personal shares in SVB and was by no means invested. Nevertheless, this incident positively raises new studying factors for us buyers to be aware of. Whereas watching the disaster unfold, the largest query in the back of my thoughts was whether or not retail buyers might have foreseen this, and thus prevented their losses.
[ad_2]
Source link