[ad_1]
A new article on Bank Underground, which publishes employees papers written by personnel working on the Financial institution of England, is attention-grabbing. Written by Galina Potjagailo, Boromeus Wanengkirtyo and Jenny Lam, it focuses on the underlying causes of inflation. Its opening premise is that this:
The current rise in UK inflation was initially fuelled by two large external shocks: supply bottlenecks along global value chains as a result of Covid-19 (Covid) pandemic (for example, with microchips and used vehicles) and hovering vitality and meals costs associated to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Having then famous that the costs in query are set externally to the U.Ok. the authors counsel:
Nonetheless, broader home worth will increase through ‘second-round results’ can comply with as a result of vitality costs have an effect on the prices of many different items and companies by way of their function as indispensable enter in manufacturing and transport.
To this point, so good, and I agree. The second declare cannot be disputed in some circumstances, though its significance might be.
What they do subsequent is attention-grabbing. What they argue is that there are 4 causes of inflation proper now:
- The Ukraine battle
- Covid reopening (which they assume is now taken over by a battle impact, however could also be persevering with)
- Idiosyncratic inflation e.g. that in second-hand automotive costs due to shortages of chips to make new vehicles
- Remaining inflation (underlying inflation, or UIM as they name it). This could embrace secondary results from the above.
The break up makes some sense, though it’s unsophisticated on secondary impacts with out trigger being established.
Their first iteration of that is as follows:

As they observe:
In September, the historic underlying inflation measure (crimson bars) has reached 5.8%, the very best degree noticed over the pattern interval, having elevated by 3.6 proportion factors in cumulated phrases since early 2021.
They add:
It’s … corresponding to the Federal Reserve’s estimates of US underlying inflation (6.0% for September).
However they don’t then settle for this as the ultimate reply on underlying inflation. As they observe:
The majority of the rise in underlying inflation is because of broad-based vitality worth will increase, suggesting that vitality costs have more and more comoved with different costs. Chart 3 decomposes the cumulated improve in UIM, the Covid and Russia-Ukraine battle results since March 2021 (total 8.8 proportion factors). Virtually two thirds of this improve got here from broad-based will increase in vitality objects’ costs (5 proportion factors), and a a lot smaller contribution of 1.3 proportion factors got here from broad-based will increase in meals costs.
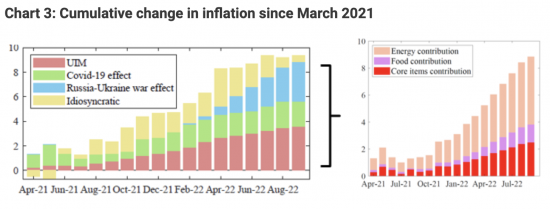
They argue:
These broad-based will increase in vitality and meals objects contributed not solely to the extra erratic Covid and Russia-Ukraine battle results, but in addition to the UIM. The results on underlying inflation ought to, in precept, decay as soon as the exterior shocks behind vitality and meals worth spikes subside.
They’re fairly clear that they anticipate this to occur:
The results of those elements ought to fade out comparatively shortly as the 2 shocks subside – we due to this fact view them as one other sort of erratic part relatively than as a part of underlying inflation.
In different phrases, they’re fairly certain that as the primary a part of Chart 3 exhibits, core inflation is at current below 4%, and because the second half exhibits, as soon as the influence of battle (specifically) is proscribed within the calculation of inflation (which it is going to be by mid-2023, as a result of by then inflation calculation will evaluate post-Putin battle costs with post-Putin battle costs) then inflation is perhaps below 3%.
The authors then reveal their Financial institution of England colors, saying:
Nonetheless, the truth that these things have moved collectively with many different UK worth objects signifies that the exterior shocks would possibly start to propagate to home worth pressures.
I counsel ‘would possibly’ is doing quite a lot of heavy lifting in that sentence. It ought to truly say ‘ought to’, as a result of individuals might want to recuperate their buying energy. However the actuality is that the inflationary influence of that is going to ship inflation solely a bit of over the two% arbitrary goal set for it.
The authors conclude:
Our discovering of an increase in underlying inflation amongst core objects means that the inflation within the UK is partially pushed by broad-based will increase in costs which might be usually relatively secure. Over the previous, shifts on this part have been fairly persistent, so it might plausibly stay elevated. The exact hyperlink between the breadth of worth will increase and inflation persistence in a excessive inflation surroundings stays an open query related for central banks.
My suggestion is that the information strongly implies three different issues.
First, inflation will decline considerably subsequent yr. There isn’t any purpose to extend rates of interest to make that occur: it would anyway.
Second, Financial institution of England financial coverage is basically flawed in consequence: this evaluation exhibits that.
Third, the proper query to ask now’s whether or not a 2% inflation goal is affordable for the subsequent two or three years as spending energy is restored. Would not a yr at 4% and two extra at 3% make sense in that case? After which resolve if 2% would possibly ever make sense once more, I counsel. Underlying financial elements would possibly counsel it doesn’t. However proper now, utilizing this logic, inflation is actually below management and coverage ought to deal with restoring financial buying energy within the financial system – which is all all the way down to fiscal coverage. In that case, the Financial institution of England needs to be doing exactly nothing at this second.
[ad_2]
Source link














