[ad_1]
Effectively, that break didn’t final lengthy.
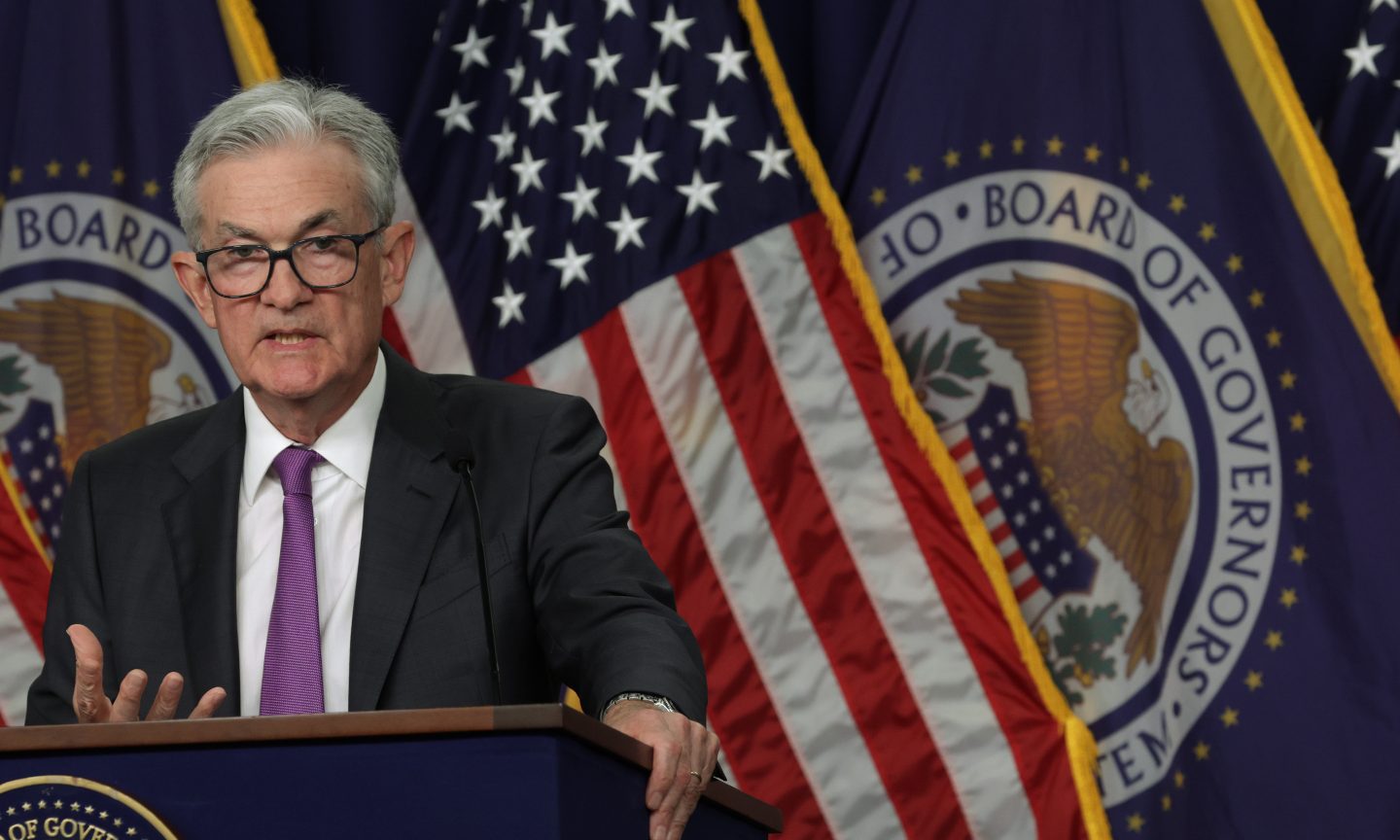
The Federal Reserve opted to resume rate hikes at Wednesday’s assembly by 1 / 4 of a share level, as anticipated. Final month, the central financial institution took a brief hiatus from growing the federal funds price after 10 consecutive price hikes starting in March 2022. The federal funds price vary is now 5.25% to five.50% — a greater than 22-year excessive.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell stated throughout a information convention Wednesday that final assembly’s pause and this assembly’s hike don’t sign the beginning of a sample to extend charges at each different assembly. Between now and the Sept. 19-20 assembly, he stated, the Fed will look carefully at 5 upcoming experiences, all from the Bureau of Labor Statistics: the employment value index report due Friday, two jobs experiences and two consumer price index (CPI) experiences.
Fed continues its pursuit of two% inflation
The CPI is used as a proxy for inflation. The June CPI report launched July 12 confirmed inflation rose 0.2% in June, up 3% from the identical month a 12 months in the past — it was the bottom stage since March 2021. The report got here in higher than anticipated, but it surely’s just one report, Powell stated.
It’s true that disinflation has begun with none actual prices to the labor market, however Powell stated he wouldn’t use the time period “optimistic” to explain this case. As a substitute, he stated present situations point out “there’s a pathway” to a delicate touchdown. Nevertheless, the Fed is now not anticipating a recession, Powell added.
Powell famous that the unemployment rate of three.6% is identical as in March 2022, when the Fed first started growing the rate of interest. “It’s not that we’re aiming to lift unemployment,” Powell stated. However he stated historical past means that, “when central banks go in and gradual the financial system to deliver down inflation, the end result tends to be some softening in labor market situations. And so that’s nonetheless the possible end result right here.”
The worst end result, Powell stated, can be to not cope with inflation now. “Regardless of the short-term value of getting inflation beneath management, the longer-term social prices of failing to take action are better,” he stated. “The historic file may be very, very clear on that.”
Powell added that if inflation just isn’t introduced down, it turns into risky, which interferes with folks’s lives and financial exercise.
The Fed chair was ambivalent about future hikes, saying the central financial institution would possibly increase funds on the September assembly if the information warrants, but it surely’s additionally attainable it may maintain regular.
Powell stated the Fed is approaching some extent the place it should steadiness the danger of doing an excessive amount of with the danger of doing too little. “As our stance has grow to be extra restrictive and inflation moderates, we do, more and more, face that threat,” he stated.
What occurs subsequent?
Very like the Fed, economists are additionally now curbing recession expectations for the approaching 12 months. In a July 15 survey by The Wall Avenue Journal, the 69 economists polled estimated that there was a 54% probability of an financial downturn within the subsequent 12 months. The final two estimates from earlier WSJ surveys have been 61%.
In the meantime, in a July 19 survey by Goldman Sachs, its economists estimated there was a 20% chance of a recession over the following 12 months, down from 25%. Goldman Sachs economists additionally collectively projected that the speed hikes through the Fed’s July assembly can be the final for this cycle.
Photograph by Alex Wong/Getty Photographs Information through Getty Photographs
[ad_2]
Source link